Researchers at IHP - Leibniz Institute for High Performance Microelectronics have set a new world speed record. The circuit designed by the scientists in Frankfurt (Oder) can transmit data wirelessly at up to 200 gigabits per second. This surpasses the previous record, last published in 2019, which was around 120 gigabits per second. The results of the development have been published in the prestigious "IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits" magazine, after being peer-reviewed by experts. A research team at IHP has thus proven for the first time worldwide the general feasibility of extremely high data transmissions in the so-called D-band (frequencies between 110 and 170 GHz) and created a basic prerequisite for realising applications for the next generation of mobile communication (6G).
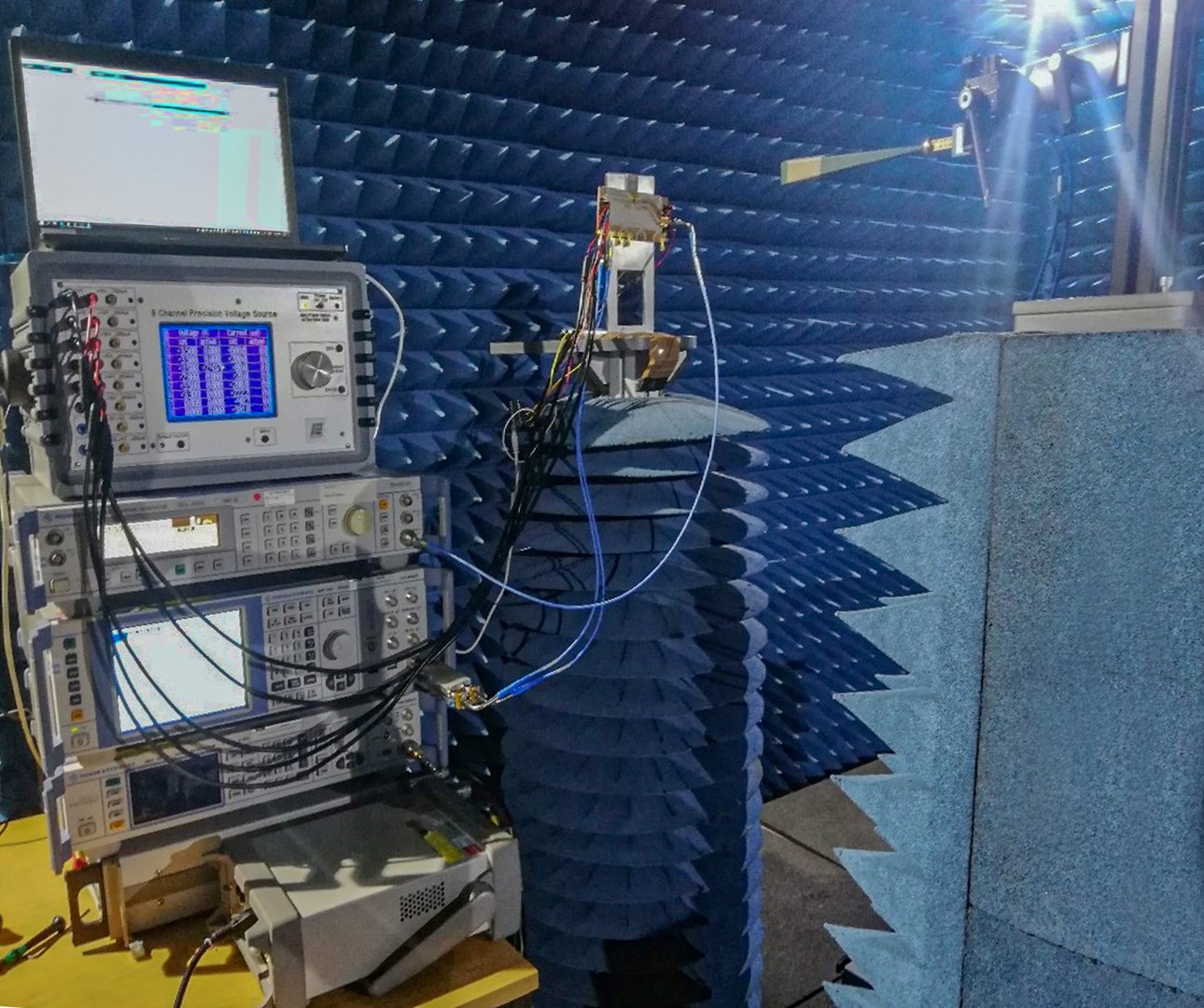
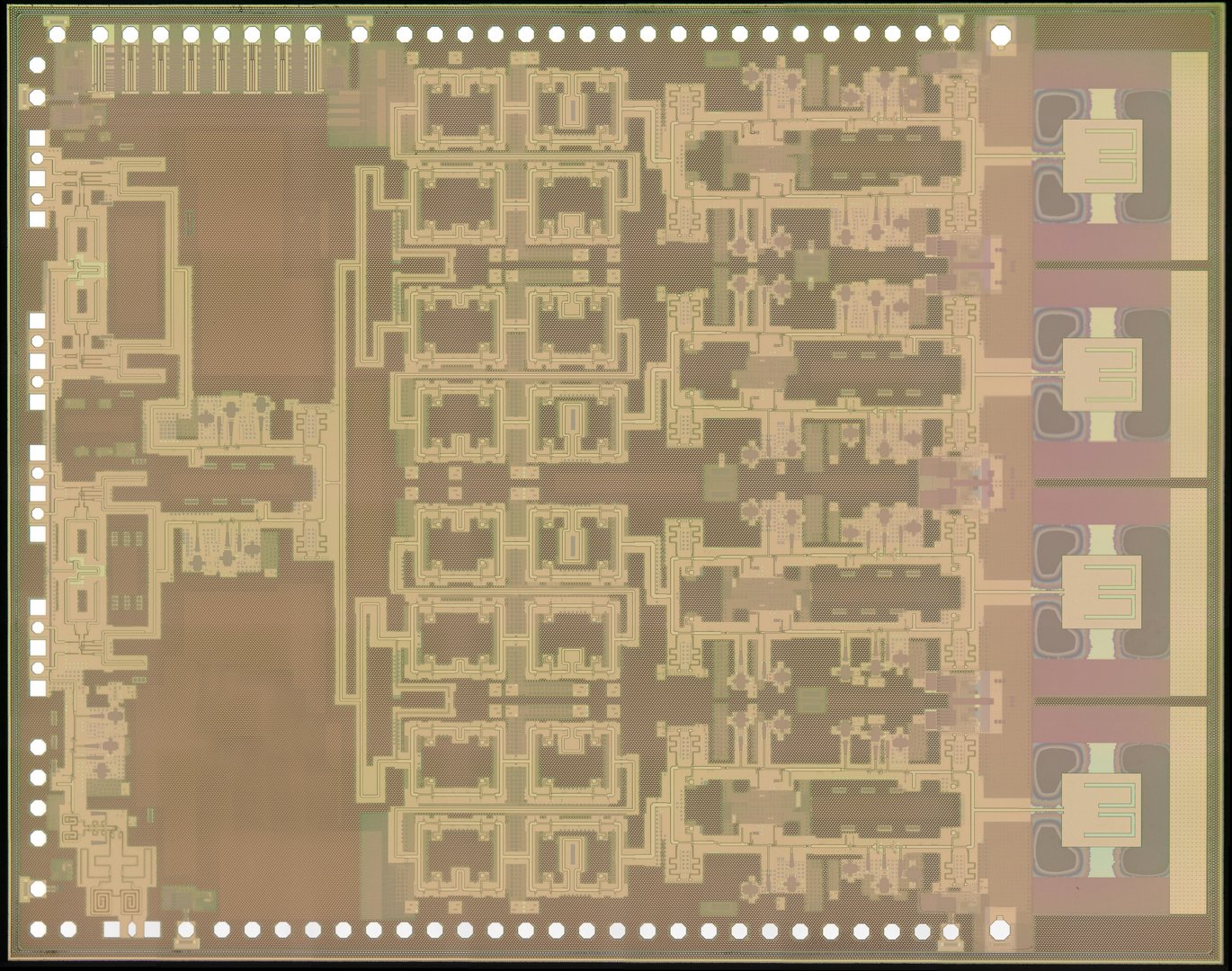
A breakthrough has been achieved by IHP scientist Alper Karakuzulu and his research group led by Dr Andrea Malignaggi. The experts in communication circuits of the highest data rates have developed a new chip within the 130 nm SiGe BiCMOS technology that contains transmitter, receiver and on-chip antennas and enables data transmission of 200 gigabits per second. "Our design was simulated down to the last detail before the circuit went into production," explains Dr Andrea Malignaggi. The microchips manufactured in the IHP clean room were then extensively tested, and their performance measured in the IHP's antenna measurement chamber, where there is no distracting radiation. The result, transmission over an initial range of 15 centimetres, is the basis for further development of the technology. "To be able to realise 6G for mobile communications, we need a completely new architecture. Picocells are an example of this. These radio cells should enable very high data rates at short distances, e.g. in conference rooms or in private areas when mobile phones, televisions and other devices are networked together," explains Dr Andrea Malignaggi. Through the further development of the integrated components and circuit blocks of the individual chip, the integration of additional antennas and the combination of several microchips into complex systems, it will be possible in the future to transmit data ultra-fast even over a greater distance.
IHP is currently contributing its expertise to two important research projects in the field of 6G development. The EU project "Open6GHub - 6G for Society and Sustainability" aims to contribute to a global 6G harmonisation process and standard in a European context. The 6G Research and Innovation Cluster, or 6G-RIC for short, is a research hub designed to lay the scientific and technical foundations for 6G across all technology levels, from radio access to core networks and fiber optic transport networks. With its research, IHP is thus making an important contribution to strengthening Germany's and Europe's technological sovereignty and position in the international competition for 6G.
The full scientific publication can be found at:
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10005812